Effective mRNA Pulmonary Delivery by Dry Powder Formulation
- 領域
- Drug Delivery
- Reference No.
- IP00852
Key Problem and Market Opportunity
- Local administration of mRNA by inhalation for the treatment of lung diseases is desirable due to its non-invasive nature, increased local drug concentration and reduced systemic side effects, hence improving treatment efficacy, especially for dry powder formations
- However, formulating mRNA into dry powder formulation is highly challenging:
- The powder must be highly dispersible and exhibit good aerodynamic properties for effective lung deposition;
- It is difficulty to maintain the integrity and biological activity of the mRNA during the drying process, considering that the long single stranded mRNA molecule is fragile and liable to thermal and shear stresses
Key Advantages of the Technology
- Dry powder formation with good aerodynamic properties
- High transfection efficiency on cells and mice
- Low risk of inflammatory response
- Applicable to existing manufacturing process, e.g. spray drying and spray freeze drying
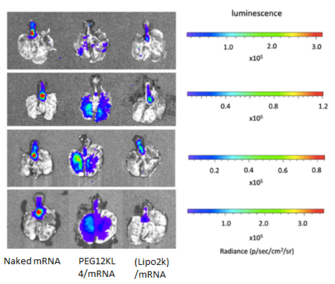
Fig. 1 Pulmonary delivery of mRNA formulations with different transfection agents
- BALB/c mice (∼20 g) were administered intratracheally with naked mRNA; PEG12KL4/mRNA complexes at 10:1 ratio (w/w); and Lipofectamine 2000 (Lipo2k)/mRNA complexes at 2:1 ratio (w/w). Each mouse received 10μg of mRNA.
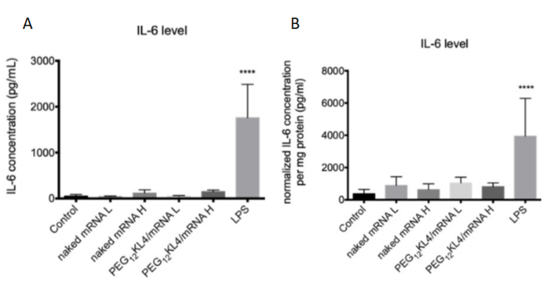
Fig. 2 Level of IL-6 following pulmonary delivery of mRNA formulations
- BALB/c mice were administered intratracheally with PBS as control; nakedmRNA L(low dose of 5μg); naked mRNAH (high dose of 10μg);PEG12KL4/mRNA L (lowdose of 5μg);PEG12KL4/mRNA H (high dose of10μg); and LPS (10μg), all in a final volume of 75μL PBS. At 24 h post-administration, IL-6 levels in (A) bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) and (B) lung homogenates were detected by ELISA. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (n = 4–6).
Further Details
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168365919305917?via%3Dihub
Potential Product and Services
- Delivery vector for therapeutic mRNA in lung diseases
- Delivery vector for mRNA vaccine
Development Status
Patents
- US provisional patent filed
IP Status
- Patent application submitted