A Dual-Functional Antiviral Peptide Inhibits Two Entry Pathways of SARS-CoV-2
- Field
- Therapeutic Biologics
- Patent
- IP00996
Key Problem and Market Opportunity
- With the widespread circulation of SARS-CoV-2 during the COVID-19 pandemic, the emergence of virus mutants and the decreasing antibody titers after recovery demonstrated the possibility of re-infection. The development of broad-spectrum antivirals is urgently needed for SARS-CoV-2 and new emerging viruses.
- According to the World Health Organization, up to 650,000 deaths annually are associated with respiratory diseases. With an escalating number of people who were hospitalized each year due to respiratory viruses, there is an urgent need to develop therapeutics which are more efficient.
- The global anti-viral drug therapy market is expected to grow from 46 billion in 2019 to 74 billion in 2023, due to the increase in number of COVID-19 cases.
Key Advantages of the Technology
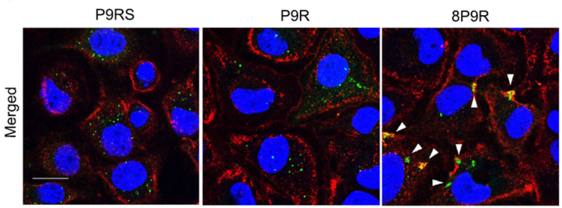
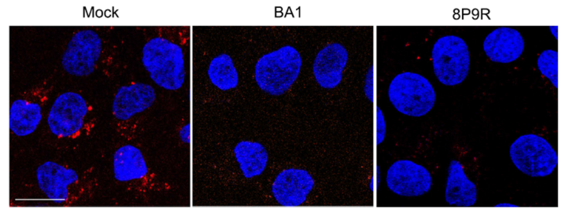
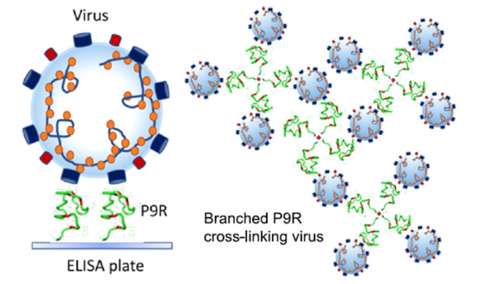
- Dual-functional antiviral peptide 8P9R:
- Cross-link viruses to block viral entry on cell surface through the TMPRSS2-mediated pathway
- Inhibit endosomal acidification to block viral entry through endocytic pathway.
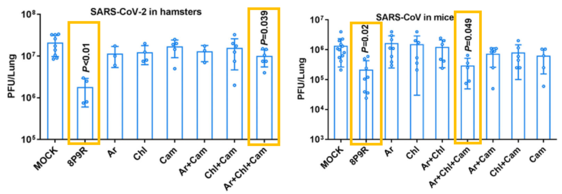
- 8P9R and the triple drug combination (arbidol, chloroquine and camostat) respectively blocked the 2 entry pathways of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV in vivo and did not induce obvious toxicity in mouse lungs.
Further Details
- Journal publication: Nature Communications (2021) 12:1517 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21825-w
Potential Product and Services
Therapeutics for COVID-19 and diseases caused by other respiratory viruses
Development Status and IP Strength
Stage of Development
- Completed animal model study
Patents
- US Prov. application. No.: 63/104,312, filed on Oct 22, 2020.
IP Status
- Patent application submitted