An Order O(1) Algorithm for Transient Current Calculation in Nanoelectronics
- Field
- Electronics
- Patent
- IP00618
Key Problem and Market Opportunity
- Response time is one of the key performance indicators of high-speed transistors in nanoelectronics
- As the response time is pushed to the limit, transient current calculation is essential in studying the response time and determining the peak transient current for preventing meltdown of the nanochips
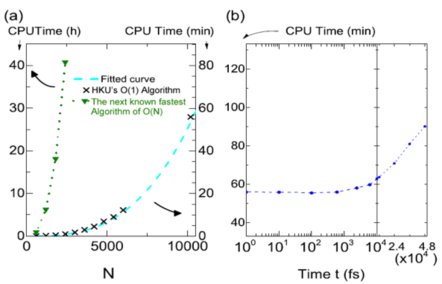
- Such calculation is known to be extremely time consuming with the best scaling complexity of TN3 (T is the number of time steps and N is the dimension of the device)
- The quantum computing software market is estimated at US$88.4 million in 2016 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 29.04% between 2017 and 2023
Key Advantages of the Technology
- A novel algorithm based on NEGF-CAP formalism is used to calculate transient current as a function of time step T; it may be further extended to NEGF-DFT-CAP formalism
- The algorithm provides an Order O(1) complexity if T < N2, where N is the system size (N usually >= 10,000)
- It is useful for designing nano-devices and predicting their actual responses before actual production
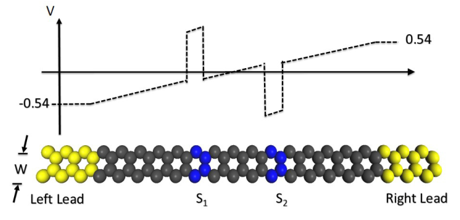
- Experiments on a gated graphene nanoribbon (Figure 1) confirmed the Order O(1) complexity with N=104 and T=108
- Such major speedup enables the application of first-principle calculations and nano-device design with ever-increasing performance requirements
Potential Product and Services
- Technology Computer Aided Design (TCAD) software for Electronic Design Automation
- Quantum Chemistry and Solid-State Physics Software
Development Status and IP Strength
- US Patent Application No. 15/424,537
- PCT Application No. PCT/CN2017/072848
- Prototype software application developed